Table of Contents
Model Construction Focus Area Summary
Model Construction Task Objective & Systems Modeling Environment Scope
- Elaborate concepts, requirements, and metrics for effective model construction that support the next generation system modeling language (SysML v2)
- Identify a set of services that support model construction, consistent with the System Modeling Environment goals
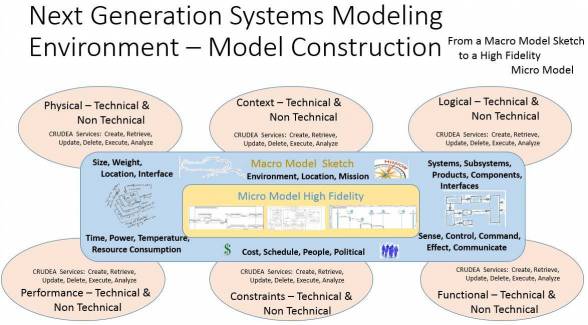
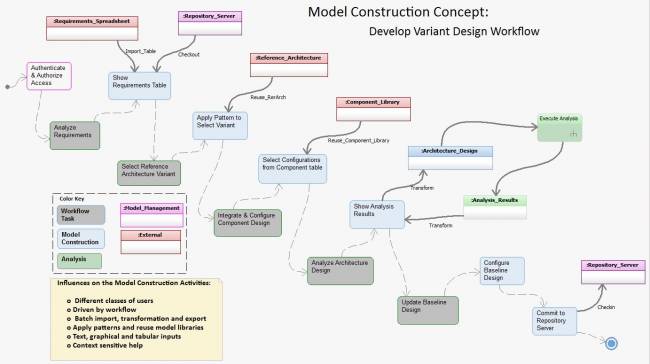
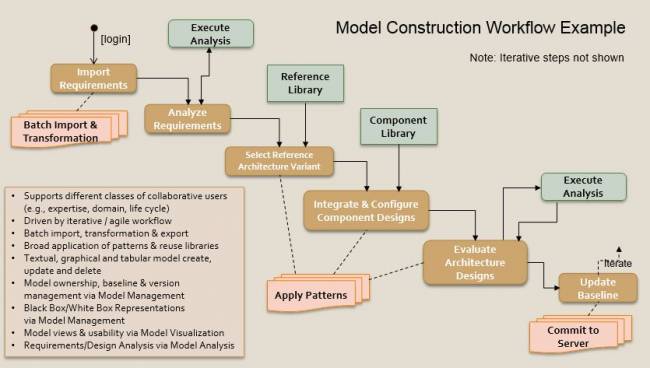
Graphics in PDF format: model_construction_graphic_rev_b.pdf
Graphics in PDF format: pdf_model_construction_concept_graphic.pdf
Graphics in PPT format:model_construction_concept_2017-03-08-b.pptx
Model Construction Systems Modeling Environment Scope
The SME (Systems Modeling Environment) Model Construction Capability will enable intuitive and efficient model construction including,
- External resources (to the SME) model inputs (for both individual model elements and model constructs and collections)
- Adaptable Novice and Expert User input support for early phase “sketch” and later phase more rigorous high fidelity models
- External data sources and tools (structured and unstructured)
- Linked data access and updates via Model Interoperability capabilities
- Query capabilities against all model elements or model constructs via Visualization capabilities via a standardized query language
- Model execution via Model Analysis capabilities
- Text (structured language or free text), tabular and graphical representations
- Support for model patterns and pattern libraries
- Extensive reuse of model element and project libraries and their contents
- Support for process easy to use implementation scripts and/or “wizards” based GUI's via Visualization and Model Management
- Support for user help facilities integral to the systems modeling environment via Visualization and Model Management
- Collaborative, team oriented model construction via Collaboration capabilities
- Controlled, role based access to the model via Model Management capabilities
- Model change management supporting new model versions and variants via Model Management capabilities
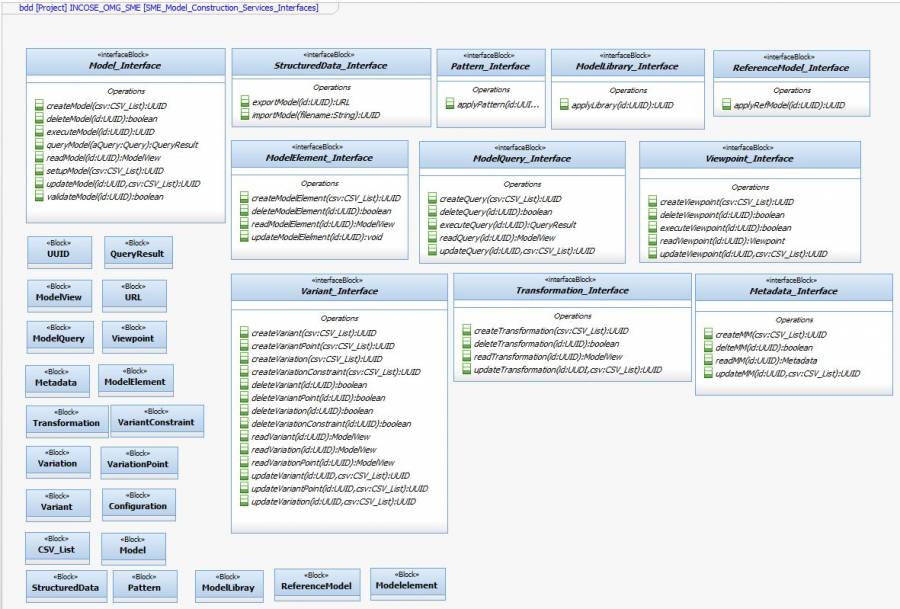
Model Construction Services Requirements
- Services to create, update, and delete
- model elements
- links between tools or file system or databases
- patterns (pattern is assumed to be a “model or model element”
- model queries (overlaps with Visualization / Model Management)
- transformations to/from SysML models (allocated to Model Management)
- Services to execute (allocated to Model Analysis)
- model elements
- patterns
- model queries
- transformations to/from SysML models
- Services to export (allocated to Model Management/Visualizatio)
- unstructured data
- structured data
Current
March, 2017 - SysML 2.0 Model Construction RFP Requirements (updated based on the March 2017 Reston workshop audience feedback)
May 2017 Model Construction Requiremnts Document
Some of the feedback included.
- A core requirement is to create, update, and delete a data set with 1 or more data elements
- Replace the service requirement to import and transform multiple elements in batch mode with a transaction service. This includes a requirement to read a list of structured data elements and its associated schema, and another requirement to transform the structured data to model elements.
- When creating an element or other model construct, create the element id (i.e., UUID)
- When transforming structured data, optionally set the id depending on whether one is specified
- When deleting an element, ensure the final state is consistent with the deletion semantics.
- When deleting an element, retain and reserve its uuid. (This may be a model management function)
- Add a service requirement to apply a pattern.
- Consider how to construct models through elaboration and refinement to transition from one level of abstraction to another, while preserving the earlier abstraction. (Note: this may be considered a transformation of one abstraction level to another that can be viewed in different viewpoints.)
- Consider usability issues that were identified in the usability discussion below
Action: Ron to update model construction service requirements with pre and post conditions. Send requirements to Geoffrey Biggs and Andy Ko for review.
1. Model Construction Functional Requirements for the Systems Modeling Environment (SME)
- 1.1 Functional Requirements Overview
- Model construction is the ability to create, update, and delete individual model elements or sets of model elements or model constructs including metadata elements.
- Model construction applies to model patterns, queries, rules and expressions, transformations, links to external data elements, interface layers, and any other constructs that are used to support the construction of the system model.
- The goal is for the SysML v2 specification to enable adaptable, efficient and intuitive model construction for a broad range of users (novice to expert). SysML v2 should not limit the use of current and future technologies that support model construction.
- Model construction can be performed in complementary ways that include
- interactively, using the adaptable graphical interface provided by the modeling environment via Visualization Services.
- data group mode, by importing data/resources from an external file, database or software application, and transforming it to the corresponding SysML model constructs.
- The model may be constructed using different forms that include textual, graphical, or tabular entry or a combination.
- The requirements for model construction have interdependencies with other requirements related to model visualization, model management, workflow and collaboration, and model analysis.
- Model construction uses services provided by these other capability areas, and the other capability areas use the model construction services.
- It is expected that all interactions with the SME be in the context of a transaction that provides the ability to ensure all SME operations are either completed successfully or the SME can be rolled back to a prior consistent state.
- Deletion Semantics: It is expected that the submitters will define the semantics associated with the deletion of model elements or constructs.
- 1.2 Create
- SysML v2 shall provide the ability to create model elements and other model constructs interactively via Visualization Services using textual, graphical, and/or tabular entry.
- SysML v2 shall provide the ability to create a set of model elements and other model constructs from an external source, and transforming the source data to the corresponding model elements or constructs being created.
- SysML v2 shall create the element id (e.e. UUID) when crating an element or other model construct.
- SysML v2 shall optionally set the element id depending on whether one is specified, when transforming structured data.
- 1.3. Update
- SysML v2 shall provide the ability to update model elements and other model constructs interactively via Visualization Services using textual, graphical, and/or tabular entry.
- SysML v2 shall provide the ability to update a set of model elements and other model constructs based on data obtained from an external source, and transforming the source data to the corresponding model elements or constructs being updated.
- 1.4 Delete
- SysML v2 shall provide the ability to delete model elements and other model constructs interactively via Visualization Services using textual, graphical, and/or tabular entry.
- SysML v2 shall provide the ability to delete model elements and other model constructs based on data obtained from an external source, and transforming the source data to the corresponding model elements or constructs being deleted.
- SysML v2 shall preserve the unique identifiers (UUID) for the deleted model elements and constructs
- SysML v2 shall define model element and construct deletion semantics.
- SysML v2 shall ensure the final state is consistent with the deletion semantics, when deleting a model element or construct.
- 1.5 Apply
- SysML v2 shall provide the ability to apply patterns, model library content, or other model element source data to the model under construction.
- 1.6 Crosscutting
- SysML v2 shall manage unique identifiers for all model elements and constructs.
- SysML v2 shall provide a transaction mechanism for all operations on the system modeling environment.
- SysML v2 shall consider how to construct models through elaboration and refinement to transition from one level of abstraction to another, while preserving the earlier abstraction. (Note: this may be considered a transformation of one abstraction level to another that can be viewed in different viewpoints.)
- SysML v2 shall consider usability issues as defined in the usability section of the SysML v2 RFP.
2. Model Construction Service Interface Requirement
- 2.1 Service Requirements Overview
- Model construction services further specify each of the functions defined by the functional requirements above and provide a definition of the signatures associated with each of the functions.
- 2.2 Create
- Pre Condition: Model element being created does not exist with the specified id (i.e. UUID)
- Post Condition: The model is updated to include the new model element and remains in a consistent state.
- return value: Single UUID or collection of UUID's of the model elements that were created
- Function Name: createModelElements
- Function Parameters:
- Collection of “Attribute”, attribute type, name and value quadruplets
- Collection of operations
- “Operation” type
- return type,
- operation name and
- operation parameter type and name pairs
- Collection of “Relationship”, relationship type, relationship name and related element UUID quadruplets
- Example: createModelElements( { {Attribute, String, Name, “MyName”}, {Attribute, String, Description, “My description”}, {Operation, Integer, Sum, updatemodelelements_myuuid_myattributename1_newvalue1_myuuid_myattributename2_newvalue2)
- 2.4 Delete
- Pre Condition: Model element being deleted exists with a uniue id.
- Post Condition: The model is updated without the deleted element and remains in a consistent state.
- Return value: Boolean (true if deleted successfully, false if error condition)
- Function Name: deleteModelElements
- Function Parameters:
- Collection of UUIDs
- Example: first retrieve a collection of model element UUID's and then invoke the deleteModelElements service using the UUID collection as a parameter.
- 2.5 Apply
- Pre Condition: The pattern being applied is complete and self consistent.
- Post Condition: The model is updated to include the new pattern remains in a consistent state.
- Return value: TBD
- Function Name: applySourceData
- Function Parameters: TBD
- Example: apply a pattern from the pattern library to the current workspace and instantiate the model elements associated with the pattern.
3. Standard Modeling Languages
- SysML v2 shall provide a platform independent modeling language and selected platform specific bindings to create, read, update, and delete model queries.
- SysML v2 shall provide a platform independent language and selected platform specific bindings to create, read, update, and delete model transformations.
- SysML v2 shall provide a platform independent language and selected platform specific bindings to create, read, update, and delete expressions.
- SysML v2 shall provide a platform independent language and selected platform specific bindings to create, read, update, and delete viewpoint methods.
4. Model Construction Concept Definitions
- 4.1 Concept Definitions Overview
- The concepts defined in this section clarify the meaning of terms used in the requirements sections above.
- 4.2 Core concepts related to model construction
- Model - (refers to existing definition)
- Model Element – (refers to existing definition)
- Model Construct – A model element or other entity used to construct a system model that includes model patterns, queries, rules and expressions, transformations, and links to external data elements
- Model Collection - A collection of model elements and/or modeling constructs used to construct the system model
- UUID (Universal Unique Identifier) - A globally unique identifier for each model element (refer to existing definition?)
- Interactive - User initiated operations using the graphical interface of the SysML user interface
- Batch Mode - User initiated operations using an external collection of model element properties, operations and- or relationships
- External (Resource) Collection - A file based or database or link based mechanism to persist descriptions of model elements
- Transaction - A mechanism to ensure an operation applied to the SME maintains the SME in a consistent state.
- Deletion Semantics - The rules associated with deletion of model elements or constructs.
December, 2016
Model Construction Service Specifications
| SME Access Point | Service | Description | Inputs | Input Types | Output | Output Types | In Out |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model Editor, External Interface | createModel | Creates a SysML model based on a set of ModelElement descriptors | Set of ModelElement Descriptors | Descriptor | Link to the Model | ModelLink | In |
| Mode lEditor, External Interface | createModelElement | Creates a SysML ModelElement based on a ModelElement description (the model element can be a node or a relationship | ModelElement Descriptor | Descriptor | Link to the Model Element | ModelLink | In |
| Model Editor, External Interface | createProject | Creates a new SysML project as a collection of SysML models | Project Descriptor | Descriptor | Link to the Project | ModelLink | In |
| Model Editor, External Interface | createPattern | Creates a new SysML Pattern as a sub model (ie. model elements and relationships) | Pattern Descriptor | Descriptor | Link to Pattern | ModeLink | In |
| Model Editor, External Interface | createLibrary | Create a new SysML model library. | Library Descriptor | Descriptor | Link to Library | ModeLink | In |
| Model Editor, External Interface | createVariationPoint | Create a new VariationPoint. | VariationPoint Descriptor | Descriptor | Link to VariationPoint | ModeLink | In |
| Model Editor, External Interface | createVariation | Create a new Variation | Variation Descriptor | Descriptor | Link to Variation | ModeLink | In |
| Model Editor, External Interface | createConfiguration | Create a new Configuration | Set of Variation Descriptors | Set of Descriptors | Link to Configuration | ModelLink | In |
| Model Editor, External Interface | createVariationConstraint | Create a new VariationConstraint | VariationConstraint Descriptor | Descriptor | Link to VariationConstraint | ModeLink | In |
| Model Editor, External Interface | createView | Create a new View | View Descriptor | Descriptor | Link to View | ModeLink | In |
| Model Editor, External Interface | createViewpoint | Create a new Viewpoint | Viewpoint Descriptor | Descriptor | Link to Viewpoint | ModeLink | In |
| Model Editor, External Interface | delete*FromModel | Delete any * (created element(s)) from the model and project | Links to model element | Set of ModelLink | Boolean return (0==failure, 1==success) | Boolean | In |
| Model Editor, External Interface | remove*FromDiagram | Remove any * (created element(s)) from a diagram | Links to diagram and model element(s) | Set of ModelLink | Boolean return (0==failure, 1==success) | Boolean | In |
| Model Editor, External Interface | update* | Update the features (e.g. attributes, operations, parts, constraints and/or relationships) of an existing model element. | Link to model element and Set of model element descriptors | ModelLink, Set of Descriptors | Link to Model Element | ModelLink | In |
| Model Editor, External Interface | updateAdd* | Update the referenced model element by adding new features | Link to model element and Set of model element descriptors | ModelLink, Set of Descriptors | Link to Model Element | ModelLink | In |
| Model Editor, External Interface | updateDelete* | Delete the features of a referenced model element. | Link to model element and Set of model element descriptors | ModelLink, Set of Descriptors | Link to Model Element | ModelLink | In |
| Concept Name | Description |
|---|---|
| ModelElement | Defined in Concept Model as any generic SysML model element including (Diagram, Block, ConstraintBlock, InterfaceBlock, Part, Activity, Action, State, Port, Pin, Association, Dependency, etc.…) |
| Model | A complete and consistent set of Model elements |
| Project | A collection of SysML models, libraries, profiles, etc. That can be persisted (e.g. in the file system, repository, library, etc.) |
| Descriptor (Primitive) | A collection of name / value pairings that fully describes a concept from the Concept Model (e.g. type: Block, name: myBlock, description: myDescription, etc.) |
| Set (Primitive) | A collection of descriptors (e.g. Set: (setName: mySet; (Model Descriptor), (Model Descriptor), (Model Descriptor),…) ) |
| ModelLink | A UUID/URL reference that can be used to access a model (as a collection of model elements) or individual model elements |
| Create | Creation of a new concept in SysML via two access points: Model Editor (assumes visualization mechanism to capture the “Descriptor” information and feed to the service interface and External Interface (assumes a service API that provides the “Descriptor” information as a collection of attribut/value pairs. |
| Update | |
| Delete |
Previous
Update (September, 2016)
Model Construction Functional Requirements Summary
The next-generation modeling language and tools shall
- enable more intuitive and efficient model construction where intuitive is defines as: when users understand the user interface behavior and effect without use of reason, experimentation, assistance, or special training; and efficient is defined as: when users are enabled to perform an action with a minimum amount of effort.
- minimize clicks to capture a core concept in a model.
- include a more streamlined and efficient user interface in order to reduce the time and effort to build and maintain a model.
- provide the ability to repeat common modeling patterns with reduced user input (e.g., table-based entry) in order to increase modeling productivity and understanding.
- enable the import of external model data from files (text, tables, databases, graphics, graph formats)
- enable the import of external model data from other tools
- enable the import of external model data from other repositories (e.g. PLM or PDM)
- enable linked data references
- enable text and graphical representations of the model
- provide for extensive use of libraries
- support process implementation mechanisms (e.g. wizards, automation scripts)
- provide for user help facilities integral to the systems modeling tasks
- provide for a collaborative, team oriented model construction environment
- provide controlled, role based access to the model
- provide for model change management supporting new model versions and variants
- provide for constructing a model in a visual graphic language format
- provide for constructing a model in a standard textual language format
- enable the creation, deletion and update of model queries
- enable the creation, deletion and update of model validation rules
- enable the creation, deletion and update of model patterns
- enable the creation, deletion and update of viewpoints and views
- enable the creation, deletion and update of analytic models
- enable the creation, deletion and update of workflow scripts
- enable the creation, deletion and update of model based notifications
Model Construction Measures of Effectiveness
- Ability to efficiently and intuitively construct models
- Efficiency metrics
- Mouse/Keyboard interactions (e.g. # interactions to create, delete, modify model element, pattern, variant or model validation rule)
- Lifecycle task productivity (e.g. requirements linking, use case behavior modeling)
- Bulk data load rate (e.g. model elements/sec)
- “Intuitive” Metrics
- Learning Curve (e.g. time and complexity)
- Tailorability to Organizations Processes/Procedures (e.g. OOSE, Harmony, SYSMOD tailoring)
- Utility of “Help” functions
- Effectiveness of standardized symbology or concrete syntax to distinguish model elements (e.g. action vs state)
- Level of support for visual graphic and textual orientations of users
- Level of alignment with industry user interface and modeling standards
- Level of tool and tool vendor coupling of model construction techniques
- Flexibility of model construction capabilities related to user experience level (novice to expert)
Model Construction -- Working Definitions of Intuitive and Efficient
Efficient
Source: http://www.uxdesignedge.com/2010/06/intuitive-ui-what-the-heck-is-it/
Definition: A UI is efficient when users are enabled to perform an action with a minimum amount of effort
A UI is efficient when it has an appropriate combination of:
- Efficiency The UI enables users to perform an action with a minimum amount of effort. If the intention is clear, the UI delivers the expected results the first time so that users don’t have to repeat the action (perhaps with variations) to get what they want.
- Contextual The UI enables a well defined context or state associated with the task at hand. If the user is within a specific diagram workspace, only those operations associated with that diagrams context are available. All non-relevant commands/operations/graphics/etc. are filtered out of the view based on the diagram context. If the user focuses on a specific model element (either within the model browser, command palette or diagram work area) via a mouse button click or touch point, only those commands relevant to the model element in context of the browser, diagram or palette appear in a “pop up” command window. All other commands/operations are filtered out.
Intuitive
Source: http://www.uxdesignedge.com/2010/06/intuitive-ui-what-the-heck-is-it/
Definition: A UI is intuitive when users understand its behavior and effect without use of reason, experimentation, assistance, or special training.
A UI is intuitive when it has an appropriate combination of:
- Affordance Visually, the UI has clues that indicate what it is going to do. Users don’t have to experiment or deduce the interaction. The affordances are based on real-world experiences or standard UI conventions.
- Expectation Functionally, the UI delivers the expected, predictable results, with no surprises. Users don’t have to experiment or deduce the effect. The expectations are based on labels, real-world experiences, or standard UI conventions.
- Efficiency The UI enables users to perform an action with a minimum amount of effort. If the intention is clear, the UI delivers the expected results the first time so that users don’t have to repeat the action (perhaps with variations) to get what they want.
- Responsiveness The UI gives clear, immediate feedback to indicate that the action is happening, and was either successful or unsuccessful.
- Forgiveness If users make a mistake, either the right thing happens anyway or they can fix or undo the action with ease.
- Explorability Users can navigate throughout the UI without fear of penalty or unintended consequences, or of getting lost.
- No frustration Emotionally, users are satisfied with the interaction.
Previous Update (June, 2016)
Model Construction OMG Orlando June 2016 Update
- Status of the effort (including whether Wiki is current)
- Wiki is current
- Updates made to Concept Model references SECM Concepts
- Suggest a Use Case / Services driven walk through of the Concept Model by each lead to check for completeness
- Link to common supporting services wiki page completed
- Services and Use Cases consistent Model Construction Use Cases
- Effectiveness measures and driving requirements
- Ease of use (model construction complexity measures)
- Automation opportunities (import of external data)
- Validation aspects (correctness, completeness of the model construction)
- Model Quality Analytics (e.g. assessment of complexity, depends on method profile employed (SysMOD, Harmony, OOSE, etc.)
- Limitations of current SysML
- Executable aspects of the system model (linkage to simulation, physics & dynamic models)
- Constraints language for typical systems engineer (beyond OCL)
- Parametrics equations (free text is inadequate….reference a standard and incorporate in tools)
- Temporal modeling (some hooks, but should go much further to adequately model “time”
- Spatial modeling (relative, logical and geospatial)
- Viewpoint and View definitions and mechansims
- Accommodation of Patterns
- Support for non-model data import (tables, text, etc.)
- Ease of creating new “sub profiles” that are tailored to problem domains (vocabulary, constraints, patterns, etc.)
- Availability of a human readable/understandable language to represent SysML (XMI is for machines not humans)
- Key features of the concept
- Automation mechanisms for structured & unstructured data import
- Linkage with advanced visualization
- Linkage with Model Management
- Linkage with Collaborative Model Development
- Service requirements (e.g. functions)
- see list at Interoperability Working group
- A complete list of services is included in the spreadsheet
- Illustration of how the concepts supports the Hybrid SuV scenario
- see explanation below Hybrid SuV scenario
Change Scenario Example - Model Construction Focus
- Plans for prototypes to demonstrate feasibility
- No plans as yet, suggest combining with Model Lifecycle Management prototype plans
Previous Update Feedback (March, 2016)
- Consider combining the 3 model construction use cases for the purposes of a practical illustration. However, keep them distinct in terms of specifying the requirements on the SME.
- The 3 use cases include:
- Constructing a model from scratch
- Reusing an existing model
- Importing unstructured legacy data (e.g. word, excel)
- The idea of relating the methodology/workflow to model construction was an excellent insight.
- A specific methodology may include a combination of profiles, patterns, and wizards
- Need to differentiate the overall workflow requirements from the model construction specific requirements
- Develop a specific use case addressing the construction of a model in the context of a workflow process/engine/manager
- In model construction the services supporting task automation, pattern use, library access, model structure template access, etc. are emphasized
- In workflow, the documentation of the methodologies available, the tracing and linkage to relevant tools, the transformation of models within the workflow, and the tailorable steps necessary to complete modeling tasks are provided as services
- Provide a capability to perform a batch create, read, update, or delete to a set of model elements which are specified by some criteria (all blocks, a particular package, etc.)
- Emphasize the need to support a textual input to the model
Model Construction - Practical Illustration Use Cases
Model Construction - Batch Mode
- Provide a capability to perform a batch create, read, update, or delete to a set of model elements which are specified by some criteria (all blocks, a particular package, etc.
- Constructing a model from scratch
- Pre Condition: Patterns, Model Libraries, Model Quality Rules, System Level Requirements Tables are available
- Scenario: “Outside In” / “Top Down” Approach
- Step: Import a table of requirements as a set of “Requirement” elements (structure in packages by function, performance, SOW, etc.)
- Step: Functional Analysis. Create “System Function” elements and trace to “Requirement” elements
- Step: Architecture/Design: Create “System/SubSystem” model elements and allocate “System Functions” to each
- Step: Architecture/Design: Create state and performance attributes for each “System/Subsystem” element
- Step: Requirements Analysis: Create “Use Case” model elements and trace to “Requirement” elements
- Step: Resource Analysis: Create “Resource” and/or “Information” elements and trace to “Requirement” elements
- Step: Resource Exchange Analysis: Create “Resource Exchange” model elements and trace to “Requirement” and “System Function” elements
- Step: Use Case Analysis: Create scenarios and reference “System Function” elements for each step in the scenario
- Step: Create a process flow and data flow Views of the resulting scenario steps
- Step: Create a message sequence View of the primary and alternate scenario steps
- Step: Create a state machine View for each “System/Subsystem” element
- Step: Create “Constraint” elements with embedded parameters and equations
- Step: Create “Value Binding” relationship between the constraint parameters and element attributes
- Step: At each step in the scenario run “Validation Rule”, “Model Quality Rule” checks and correct the model if needed
- Step: Use automation to auto create ports, interfaces, connections and flows between the “System/Subsystem” elements
- Step: Execute the completed model to determine end to end completeness of the behavior threads
- Post Condition: New patterns created, New model elements created, Complete model with Requirements traceability is validated and quality checked and constraints are bound to relevant model elements
- Reusing an existing model
- Pre Condition: Existing model available in one of several formats (XMI export, Structured Text format, Repository Reference, Link to external Tool)
- Scenario: Access existing model
- Step: Authenticate with the tool and underlying model repository
- Step: Credentials allow access to model based on authorization profile
- Step: Visualize and review model elements
- Step: Add, remove, update elements as needed
- Step: Save model
- Post Condition: Updated model saved with new version identifiers, tagged with credentials of the user
- Importing unstructured legacy data (e.g. word, excel)
- Pre Condition: Unstructured legacy data available on local file system or accessible in remote repository; Content includes either Requirements, Architecture or Design Descriptions
- Scenario: Parse the legacy data based on underlying meta model (based on the SECM concepts)
- Step: Identify parsing rules for structure, behavior, requirements, parametrics, constraints, etc.
- Step: Identify the problem domain to assist in mapping to domain specific concepts (e.g. platform type, sensor, effector, communication protocols, etc.)
- Step: Generate a straw man model of the structural elements (blocks, parts, ports, interfaces) based on the legacy data descriptions
- Step: Generate a straw man model of the behavioral elements (states, sequences, messages, activities, actions, data exchanges, etc.) based on the legacy descriptions
- Step: Capture requirements (shall statements or equivalent) and “recommend” traceability links to other model elements based on context of the unstructured description
- Step: Generate constraint blocks and parameters and bind to model element properties based on context of the unstructured descriptions
- Step: Run validation, consistency, completeness model checkers on the resulting strawman model
- Step: Manually update the model to resolve model checker exceptions
- Post Condition: Completed model consistent with the unstructured requirements/architecture/design description
Model Construction - Relating Methodology/Workflow
- A specific methodology may include a combination of profiles, patterns, and wizards
- Need to differentiate the overall workflow requirements from the model construction specific requirements
- Develop a specific use case addressing the construction of a model in the context of a workflow process/engine/manager
- In model construction the services supporting modeling task automation, pattern use, library access, model structure template access, model manipulation, model transformation within a task context, etc. are emphasized
- In workflow, the documentation of the methodologies available, the tracing and linkage to relevant tools, the transformation of models across the workflow services, and the tailorable steps necessary to complete modeling tasks are provided as services
See the Workflow Wiki page at: Collaboration & Workflow Working Group
Model Construction - Textual Input
- Human Readable Language Constructs
- Map the Concept Model vocabulary into a structure language
- Context Free Grammar based
- Examples include: Modelica, OPM, AADL, etc.
- SysML as a Domain Specific Language
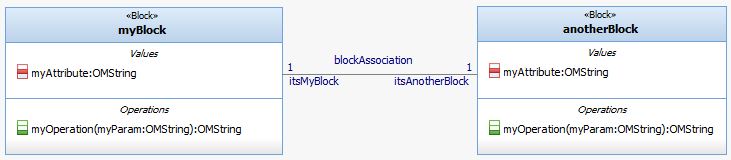
- Block myBlock { attribute: myAttribute: OMString; operaton: myOperation {returns: OMString; parameter: myParam OMString } }
- Block anotherBlock { attribute: myAttribute: OMString; operaton: myOperation {returns: String; parameter: myParam OMString } }
- Association blockAssociation from: myBlock {multiplicity: 1 roleName: itsMyBlock} to: anotherBlock {multiplicity: 1 roleName: itsAnotherBlock}
- …
- Structured Text Parsing
- Examples include System Requirements Document (outline structure and “shall” statements)
- Unstructured Text Parsing
- Natural Language Processing with a domain specific vocabulary NLP Research Example PTC Integrity Process Director
Additional Summary Material
Model Construction Context
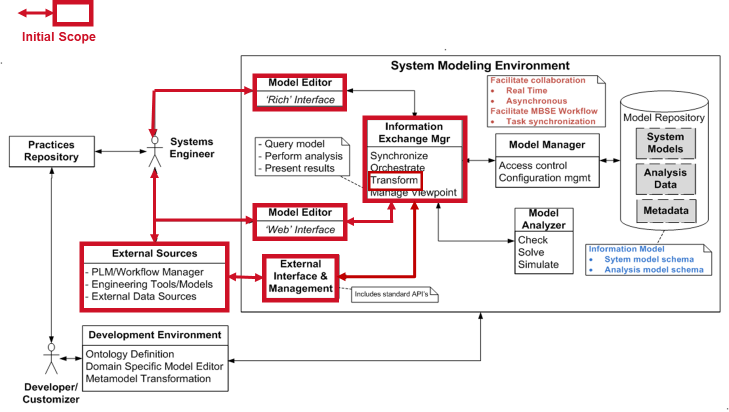
The context for the model construction use cases and services is highlighted in the following conceptual architecture for the Systems Modeling Environment (SME).
The construction of a systems model can be initiated in three basic ways: i) via a “rich” model editor client, ii) via a “web” model editor client or iii) via an external interface mechanism including programmatic (e.g. via a programming language graph representation), tabular input (e.g. MS Excel), graphics (e.g. MS Visio or PowerPoint) or textual (e.g. text document). The task of construction a system model ranges from being a purely manual process to a semi-automated process that loads the external representation of the model content, parses through the external description, transforms the description based on the System Model's concept model and/or metamodel and finally provides a visualization of the resulting model (in both textual and graphical representations.).
SysML v1.x limitations for Model Construction
- Standard is limited to model element definition for both abstract and concrete syntax
- Focuses on the “visual” programming, interactive model construction style, one element at a time
- No standards reference for importing external data (exclusive of XMI representation)..vendors take proprietary approaches (if at all)
- Emphasizes “model based” vs “document based” but doesn't address construction of the model from existing “documents”
- Defines a “rudimentary” requirement object, but does not address importing or linking to external requirements repositories or management tools
- No reference to importing from structured natural language sources such as legacy CONOPS, SRD, SSS, etc.
- No reference to importing and linking external Whole Life or Speciality/Quality Engineering models
- Much systems engineering work is done in tables / spreadsheets, no standard reference to import tabular data and link with model elements
Use Cases - Model Construction
- Systems engineers and other discipline engineers contribute to the development and update of the system model throughout the lifecycle to support system specification, design, analysis, and verification activities
- Lifecycle Phase: Meta Concept Development
- Lifecycle Phase: Concept Development
- Lifecycle Phase: Requirements Analysis
- Lifecycle Phase: Architecture Refinement
- Lifecycle Phase: System Design
- Lifecycle Phase: Analysis of Alternatives
- Lifecycle Phase: Quality Attribute Assessment
- Lifecycle Phase: Performance Assessment
- Lifecycle Phase: IV&V
- Lifecycle Phase: Transition to Development Disciplines
Lifecycle Phase: Meta Concept Development
| UseCase | ModelElements | SourceData | Tool Interoperability |
|---|---|---|---|
| Create/Update Viewpoint Definitions | Viewpoint | ISO and IEEE definitions | TBD |
| Create/Update View Definitions | View, Query, Model Reference | ISO and IEEE definitions | TBD |
| Create/Update Pattern Definitions | Model, Model Dependency, Pattern | TBD | TBD |
| Create/Update Model Library Definitions | Model, Library, Reference, | ISO and IEEE definitions | TBD |
| Create/Update User Role Definitions | User, Role, AccessControl | TBD | TBD |
Lifecycle Phase: Concept Development
| UseCase | ModelElements | SourceData | Tool Interoperability |
|---|---|---|---|
| Create/Update Capability Definitions | Capability | DoD: Capability Definition Document | MS Office, Adobe PDF |
| Create/Update Capability Dependencies | Capability, Sequence, Association, Mission, Policy, Vision, Objective | DoD: Capability Definition Document | MS Office, Adobe PDF |
Lifecycle Phase: Requirements Analysis
| UseCase | ModelElements | SourceData | Tool Interoperability |
|---|---|---|---|
| Import Requirement Objects | Requirement, Association | DoD: System Requirements Document, System/Subsystem Requirements Document | MS Office, Adobe PDF, DOORS, RequisitePro |
| Link Requirement Objects | Requirement, Association, ExternalLink | Model, External Requirements Repository | DOORS, RequisitePro |
Lifecycle Phase: Architecture Refinement
| UseCase | ModelElements | SourceData | Tool Interoperability |
|---|---|---|---|
| Create System Architecture Structure | Context, System, Subsystem, Resource, Exchange, Association | DoD: DoDAF System/Services Viewpoint | MS Office, Adobe PDF |
| Create System Architecture Behaviors | Task, Process, Function, State, Message | DoD: System/Subsystem Design Document | MS Office, Adobe PDF |
| Create System Architecture Constraints | Doctrine, Tactic, Technique, Procedure, Law | DoD: DOTMLPF | MS Office, Adobe PDF |
Lifecycle Phase: System Design
| UseCase | ModelElements | SourceData | Tool Interoperability |
|---|---|---|---|
| Create System Design Structure | Context, Component, Resource, Exchange, Association | DoD: System/Subsystem Design Document | MS Office, Adobe PDF |
| Create System Design Behaviors | Task, Process, Function, State, Message | DoD: System/Subsystem Design Document | MS Office, Adobe PDF |
| Create System Design Constraints | Design Rules | DoD: Standards | MS Office, Adobe PDF |
Lifecycle Phase: Analysis of Alternatives
| UseCase | ModelElements | SourceData | Tool Interoperability |
|---|---|---|---|
| Create/Update AoA Definitions | AoA | DoD: AoA Definition Document | MS Office, Adobe PDF |
Lifecycle Phase: Quality Attribute Assessment
| UseCase | ModelElements | SourceData | Tool Interoperability |
|---|---|---|---|
| Create/Update Quality Attribute Definitions | QA | DoD: Quality Definition Document | MS Office, Adobe PDF |
Lifecycle Phase: Performance Assessment
| UseCase | ModelElements | SourceData | Tool Interoperability |
|---|---|---|---|
| Create/Update KPP, TPM, CPM Definitions | TPM, CPM, KPP | DoD: Performance Definition Document | MS Office, Adobe PDF |
Lifecycle Phase: IV&V
| UseCase | ModelElements | SourceData | Tool Interoperability |
|---|---|---|---|
| Create/Update Test Case Definitions | TestCase | DoD: IV&V Specifications | MS Office, Adobe PDF |
Lifecycle Phase: Transition to Development Disciplines
| UseCase | ModelElements | SourceData | Tool Interoperability |
|---|---|---|---|
| Create/Update Software Architecture Definitions | SoftwareArchitecture | DoD: Software Requirements Specification | MS Office, Adobe PDF |
| Create/Update Hardware Architecture Definitions | HardwareArchitecture | DoD: Software Requirements Specification | MS Office, Adobe PDF |
SECM Concepts relevant to Model Construction Service Data Types
Model Construction Relevant Concepts (Structure):
| Name | Documentation |
|---|---|
| Component | A constituent part of an element or system that contributes to the properties and behaviors of the whole (emergent). Note: A leaf component does not have constituent parts. |
| Data | A component of information. |
| Data type | Refer to UML specification |
| Domain | A scope that encompasses a set of entities and relationships that may be addressed by the model. |
| Element | Anything of interest to the modeler, which is uniquely identifiable and can be characterized by a set of properties. |
| Environment | A collection of systems and elements that interact either directly or indirectly with the system of interest. |
| Instance | A unique model element in a set that iis defined by the general features of its classifier. |
| Interface | The inputs, outputs, ports, connections, connecting components (i.e. harness), and associated information that support one or more interactions between systems. Note: The UML definition of interface also includes the operations that must be performed in response to the inputs or invocations. |
| Mission | The operational context and purpose that the system is intended to support. |
| Model (graphical, visual) | A representation of something of interest that includes notation and semantics. |
| Model element | A construct that is used to build a model. |
| Model interchange | The ability to exchange model information. |
| Model view | A subset of model elements and associated relationships, that are of use to the modeler for a particular purpose and context. |
| Node | A component of a system that provides resources to support execution. |
| Port | The part of a system or component that provides access between a system’s behaviors and properties, and its environment. Note: this is sometimes referred to as an interaction point. |
| Resource | Any element that is needed for the execution of a function. |
| Role | Refer to System role |
| Software | A component of a system that specifies instructions which are executed by a computer. |
| Stakeholder | Individuals, groups, and/or institutions which may be impacted by the system throughout its life cycle, including acquisition, development, production, deployment, operations, support, and disposal. |
| Subsystem | A logical or physical partitioning of a system. |
| System | An element, with structure, that exhibits observable properties and behaviors. |
| System context | A depiction of the inputs and outputs between a system and its environment. |
| System role | A subset of its behaviors, properties, and structure. Note: The subset may be associated with specific interactions. |
Model Construction Relevant Concepts (Requirements):
| Name | Documentation |
|---|
| Performance requirement | A performance property a system must satsify. |
| Requirement | The capability, behavior, structure, and/or properties that a system, component, or element must satisfy. Note: This is used to establish a contract between the customer (or stakeholder) and implementer. |
| Requirement attribute | An attrirbue fo a requirement, which may include its criticality or weighting, level of uncertainty, verification status, etc. |
Model Construction Relevant Concepts (Parametrics):
| Name | Documentation |
|---|---|
| Condition | An expression with a discrete output, which is true as long as the expression evaluates true, and is false otherwise. |
| Effectiveness measure | A criterion for system optimization that is critcial to the success of the mission. Note: The criterion are often used to support trade studies to select among alternatives, as well as to optimize a given design. |
| Expression | Refer to UML specification |
| Parametric model | An analysis model which defines a set of dependent or logically grouped parametric relationships. |
| Performance property | A measure of the transformation or response of a function or behavior (i.e response time, etc). |
| Property | A quantifiable characteristic. |
| Property value | Unique state of a property. |
Model Construction Relevant Concepts (Behavior):
| Name | Documentation |
|---|---|
| Action | A non-interruptible function. Note: An action represents an atomic unit of processing or work. Actions may be continuous or discrete. Discrete actions may or may not be assumed to execute in zero time. |
| Activity | One or more related actions. |
| Behavior | The activation/deactivation of one or more functions. Note: This describes how a system interacts with its environment. Reactive behavior includes the stimulus and response. |
| Condition | An expression with a discrete output, which is true as long as the expression evaluates true, and is false otherwise. |
| Event | A noteworthy occurrence that occurs at the instant of time when a specified expression evaluates true. |
| Fork | A control operator which enables all of its outputs, when the input is evaluated true. |
| Function | A transformation of inputs to outputs that may include the creation, monitoring, modification or destruction of elements, or a null transformation. |
| Input/Output | An element that is subject to a transformation by a function. |
| Interaction | Emergent behavior that results from two or more dependent behaviors Note: A system or component interacts with other components its environment, to yield an emergent system behavior from the individual component behaviors . |
| Iteration loop | A specialized loop where the loop repeats a specified number of times. |
| Process | A set of inter-related functions and their corresponding inputs and outputs, which are activated and deactivated by their control inputs. |
| Sequential state | A state which can only be active when the other sequential states are not active. |
| Simple state | A state that does not have nested states. |
| State (finite) | A condition of a system or element, as defined by some of its properties, which can enable system behaviors and/or structure to occur. Note: The enabled behavior may include no actions, such as associated with a wait state. Also, the condition that defines the state may be dependent on one or more previous states. |
| Test scenario | A scenario which replicates the behavior of the environment that interacts with the system under test. |
Model Construction Relevant Concepts (Relationships):
| Name | Documentation |
|---|---|
| Association | Refer to UML specification |
| Connection | Identification of which ports connect to one another. |
| Decomposition | A description of a whole in terms of its component parts. |
| Dependency | A relationship where a change to one entity results in a change to the other. |
| Generalization | The factoring of common features to characterize a more general concept. |
| Parametric relationship | A dependency between properties, such that a change to the value of one property impacts the value of the other property. |
| Requirement allocation | The assignment of a requirement to an element, component, or system. |
| Requirement traceability | The relationship between a source requirement and the derived requirements needed to satisfy the source requirement. |
| Requirement verification | A comparison between a requirement and the verification results that is intended to satisfy the requirement. |
| Spatial representation | A geometrical relationship among elements. |
| Specialization | A classification of an entity (e.g., element, system, function, requirement, …), which specifies the common features of the more general element, and unique features of the specific element. |
| System hierarchy | A decomposition of a system and its components. |
| System interconnection | The connection between systems and between components. |
| Transition | Response to events/conditions, which triggers a behavior. |
Model Construction Relevant Concepts (Primitive Data Types):
| Name | Documentation |
|---|---|
| Boolean | Refer to UML specification |
| Complex Number | A number which can includes a real and imaginary part. |
| Enumerated value | Refer to UML specification |
| Geometric model | A model of the geometric relationships associated with one or more elements. |
| Integer | A whole number |
| Mean | The expected value associated with a probability distirbution. |
| Physical property | A physical characteristic of a system or element (i.e. weight, color). |
| Probability Distribution | A mathematical function which defines the likelihood of a particular set of outcomes. |
| Real number | A number which can have any value from negative infinity to infinity. |
| Spatial Property | ?? Note: Representation of Primitive Location Types e.g. Geographic lat-log, Relative x-y-z |
| String | A value represented by alphanumeric characters. |
| Time Property | A property of the model that represents a local or global time, which other properties may depend on. Note: The property can support continuous or discrete-time models. This variable should not be confused with the measured or computed time that an actual system uses, which depends on a number of implementation specific factors related to clocks, synchronization, etc. |
| Variance | A measure of the distribution about the mean of a probability distribution. Refer to the mathematical definition associated with a probability distribution. |
| Vector | A data type, which specifies a magnitude and direction. |
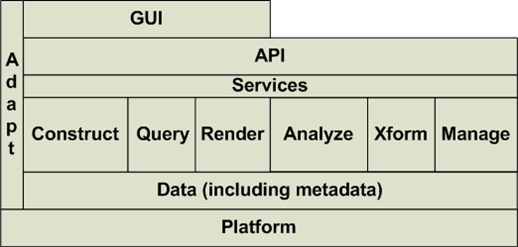
Services - Model Construction
System Modeling Environment
See the Interoperability Working Group Wiki Page for a complete set of Services (including Model Construction) at: Interoperability Working group
Performance: MoE - Measures of Effectiveness
- Ability to efficiently and intuitively construct models
- Efficiency metrics
- Mouse/Keyboard interactions (e.g. # interactions to create, delete, modify model element, pattern, variant or model validation rule)
- Lifecycle task productivity (e.g. requirements linking, use case behavior modeling)
- Bulk data load rate (e.g. model elements/sec)
- “Intuitive” Metrics
- Learning Curve (e.g. time and complexity)
- Tailorability to Organizations Processes/Procedures (e.g. OOSE, Harmony, SYSMOD tailoring)
- Utility of “Help” functions
- Effectiveness of standardized symbology or concrete syntax to distinguish model elements (e.g. action vs state)
High Level Intent / Driving Requirements
- The next-generation modeling language and tools must enable much more intuitive and efficient model construction.
- It often requires several clicks to capture a core concept in a model.
- More streamlined and efficient user interfaces could reduce the time and effort to build and maintain a model.
- The ability to repeat common modeling patterns with reduced user input (e.g., table-based entry) is another capability to increase modeling productivity and understanding.
Change Scenario Example - Model Construction Focus
The following Hybrid SUV Change Scenario will be used to illustrate the concept:
- Vehicle design unable to meet a requirement (e.g., stopping distance, safety, stability)
- Propose Requirement Change
- Assess potential impact
- Propose update to system design
- Implement/update design
- Verify system meets requirement
Vehicle design unable to meet a requirement (e.g., stopping distance, safety, stability)
Assumption: Assume physics based analysis / simulation run: From the design model, generate the simulation, get results, compare with original requirements Model Construction: (Services, Description) (Query, Inspect design features) Determine design features relevant to the requirement (Export design features) Export features to analysis/simulation tool (Import assessment) Import assessment (Link assessment) Link the assessment to the requirement and design features
Propose Requirement Change
Assumption: Change could be functional, performance, environmental Model Construction: (Services, Description) (Create req variant) Create a variant of the requirement
Assess potential impact
Assumption: Original requirement, requirement dependencies and design features are the starting point Model Construction: (Services, Description) (Create Temporary Working Viewpoint) Gather all dependent model elements into a working package (Update change impact flag and note) Determine impact on other requirements (Update change impact flag and note) Determine impact on design features
Propose update to system design
Assumption: Two paths to get here, i) no requirement change or ii) requirement change, leading indirectly to a design change. Model Construction: (Services, Description) (Append proposed change request) Append proposed change requirest to relevant design features (Generate CM change notification) Notify the CCB of the proposed change (Query proposed change package) CCB gathers relevant change information to assess impact (Approve change) CCB approves proposed changes (Deny change) CCB denies proposed changes (Import CCB assessment) Import the CCB assessment to the model (Link assessment) Link the CCB assessment to the requirement variant
Implement/update design
Assumption: CCB approved requirement change and subsequent design change or only the design change Model Construction: (Services, Description) (Add new baseline requirement) Requirement variant added to the baseline, overriding the original requirement (if needed) (Create design feature variant) Update the design baseline with new design features variants to reflect the CCB approved changes
Verify system meets requirement
Assumption: Existing test suite updated to reflect design changes Model Construction: (Services, Description) (Create test plan variant) Test plan may need to be updated (assuming the plan is in the model) (Create test scenario variant) Test scenarios may need to be updated (assuming the ascenarios are represented in the model) (Create test procedure variant) Test procedures may need to be updated (assuming the test procedures are represented in the model) (Verify system design) Execute any relevant system tests to ensure verification
Resources
References
| Date | Author | Description | Web Link |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2000 | Hubert Hofmann | Requirements Engineering: A Situated Discovery Process | http://www.amazon.com/Requirements-Engineering-Discovery-Information-IV-Controlling/dp/3824472155/ |
| 2012 | Drechsler, Soeken & Wille | Formal Specification Level: Towards Verification-driven Design based on Natural Language Processing | http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpl/login.jsp?tp=&arnumber=6336984&url=http%3A%2F%2Fieeexplore.ieee.org%2Fiel5%2F6330712%2F6336975%2F06336984.pdf%3Farnumber%3D6336984 |
| 2015 | Tao Yue | Applying A Restricted Natural Language Based Test Case Generation Approach in An Industrial Context | http://www.simula.no/publications/applying-restricted-natural-language-based-test-case-generation-approach-industrial |
Documents
Construct SE Model Overview - August 2015
Formal Specification level: Towards Verfication-driven Design Based on natural Language Processing
Construct SE Model Overview - August 2015
The Model Construction Focus Area Team
| Name | Organization | |
|---|---|---|
| Ron Williamson | Raytheon | ron_c_williamson@raytheon.com |
Ongoing Research and Product Development
| Name | Organization | Web Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tao Yue | Simula Research laboratory | tao@simula.no | http://www.simula.no/people/tao |
| Manas Bajaj | InterCAX | manas.bajaj@intercax.com | http://intercax.com/products/syndeia/ |
| Drechsler, Soeken & Wille | University of Bremen | drechsle@informatik.uni-bremen.de | http://www.informatik.uni-bremen.de/cms/detail.php?id=82 |