User Tools
Sidebar
Add this page to your book
Remove this page from your book
2.3.1.1 Centralized Network Topology
return to Network Topology Taxonomy
The centralized network topology (usually associated with mainframes) has a very large centralized server node that all other nodes connect to. It provides most of the services such as data storage, processing, backups, and computational power for the other nodes. It is possible to implement a “ledger” using the centralized model. In many ways, the centralized model that holds a single ledger is easier to implement and maintain since there is only one version of the data in one place and consequently, by definition, the data is the canonical data (i.e., authoritative or standard data).
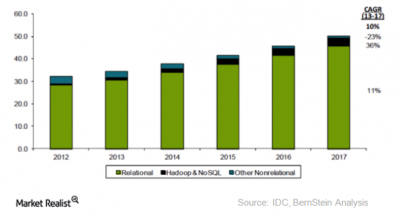
Trying to remove redundant, replicated, or duplicate data is a fundamental principle of the centralized model. The multiple “copy of data” problem was first formally addressed by E. F. Codd in his development of A Relational Model of Data for Large Shared Data Banks1) and has become the cornerstone of Relational Database Management Systems (RDBMS), used extensively today in products such as Oracle Corporation’s Oracle, IBM’s DB2, or Computer Associates INGRES 2) . The following chart shows that the centralized database market is not shrinking, and by 2017 had grown to a net worth of $50 billion with no signs of change in this growing trend. 3) This highlights the magnitude of the effort to convert the world to DIDO technology. Though it may eventually happen, it’s going to take a long time.